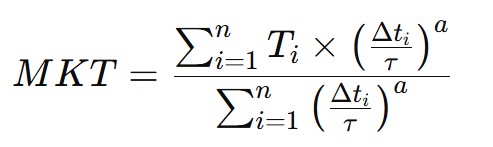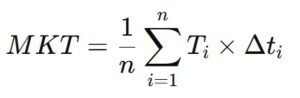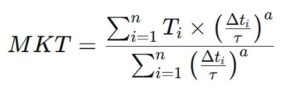Mean Kinetic Temperature (MKT): A Scientific Explanation
What is Mean Kinetic Temperature (MKT)?
Mean Kinetic Temperature (MKT) is a calculated value that estimates the overall impact of temperature variations on temperature-sensitive products during storage and transportation. In other words, MKT represents an equivalent average temperature that simulates the effect of temperature fluctuations on a product over its lifecycle, taking into account not only the extreme temperatures but also the duration of each exposure.
MKT is particularly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biopharmaceuticals, food, and other sectors where products are sensitive to temperature changes. These products can undergo chemical or physical alterations due to temperature fluctuations, compromising their quality, effectiveness, or safety. MKT provides a better understanding of the global thermal impact on these products, even if the actual temperature varies over time.
Why is MKT Important?
MKT is a valuable indicator in evaluating the integrity of temperature-sensitive products. Unlike simple average temperature, which does not account for temperature variations or their duration, MKT takes into consideration the cumulative effect of temperature fluctuations, assigning more weight to periods of higher temperatures, which are generally more damaging to the products.
This indicator helps manufacturers, distributors, and regulators determine if a product has been exposed to temperature conditions that could affect its characteristics (such as stability, effectiveness, or safety) during transport or storage. Moreover, in industries dealing with products like medications, vaccines, or perishable goods, MKT provides a reliable method to ensure that products remain within required temperature ranges throughout their supply chain.
How to Calculate MKT?
The calculation of Mean Kinetic Temperature involves using a formula that combines measured temperatures at various times and the duration of exposure to those temperatures. The standard formula used to calculate MKT is as follows:
- T_i is the temperature measured at time i (expressed in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit).
- Δt_i is the duration for which temperature T_i was maintained (expressed in hours, minutes, or seconds).
- n is the number of measurements taken during the studied period.
However, for a more precise calculation of MKT, especially when considering the effect of each temperature variation on the product’s stability, a formula that incorporates the concept of thermal activation factor (often based on Arrhenius-type equations) is commonly used. The more advanced formula, integrating this factor, is:
- T_i is the temperature measured at a given moment,
- Δt_i is the duration of exposure to that temperature,
- τ is a time constant, representing the average exposure duration of the product to a given temperature,
- a is an empirical parameter that represents the product’s sensitivity to temperature variations (often estimated through laboratory studies on product stability).
This more complex model allows for weighting the impact of periods during which the product is exposed to extreme temperatures (e.g., high or low temperatures), which are typically more harmful than periods at moderate temperatures.
To simplify this process, Thermolabo offers temperature data loggers that automatically calculate MKT. These tools are designed for professionals who demand traceability and precision in temperature monitoring.
Practical Applications of MKT
Mean Kinetic Temperature is widely used in industries where thermal management is critical. In the pharmaceutical field, for instance, medications or vaccines requiring strict cold chain management can be monitored using MKT. If the temperature exceeds specified limits for a significant duration, MKT can indicate a risk of product degradation.
In the food industry, MKT is used to ensure that perishable goods such as meat or dairy products are stored and transported at safe temperatures, preventing bacterial growth and other temperature-related alterations.
Conclusion
Mean Kinetic Temperature (MKT) is a crucial concept for assessing the thermal impact on temperature-sensitive products. By accounting for the cumulative effect of thermal fluctuations, MKT provides a reliable method for ensuring product quality and effectiveness while meeting regulatory standards. When calculated properly, MKT offers valuable data for improving supply chain management and logistics of temperature-sensitive products, whether they are medications, food items, or other goods sensitive to temperature.